Wind turbine design plays a critical role in shaping the future of renewable energy by driving efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Wind turbine innovation is not just about making wind power more efficient; it’s about transforming how we produce, distribute, and use energy. This ongoing evolution ensures that wind energy remains a cornerstone of a sustainable and resilient global energy system.
The new designs are cheaper, less expensive to install and maintain and more efficient than traditional wind turbines also allow the turbine to generate more power with fewer parts.
The Evolution of Wind Turbines:
Wind energy has been harnessed for centuries to power sailboats and grind grains in windmills. However, the concept of converting wind power into electricity dates back to the late 19th century.
The Anatomy of a Wind Turbine:
A typical modern wind turbine consists of several key components. At its core lies the rotor, which comprises two or three blades mounted on a hub. These blades are engineered to capture the kinetic energy from the wind. When the wind blows, it causes the rotor to spin, converting wind energy into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy is then transmitted through the shaft into a gearbox, which amplifies the rotational speed and drives the generator. The generator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy, which can be fed into the power grid or used to power nearby facilities.
By pushing the boundaries of engineering and design, wind turbines are becoming a cornerstone of the global transition to clean, paving the way for a sustainable future of renewable energy.
-
Improved Efficiency
Larger and More Powerful Turbines
Gigantic Rotor Diameters: Modern turbines feature larger, lightweight rotor blades that can capture more wind energy, even at lower wind speeds. This increases their capacity to generate power in diverse locations. Turbines like the GE Haliade-X (with a rotor diameter of over 220 meters) are setting records. Larger rotor blades allow for more wind to be captured, boosting the energy output of each turbine significantly.
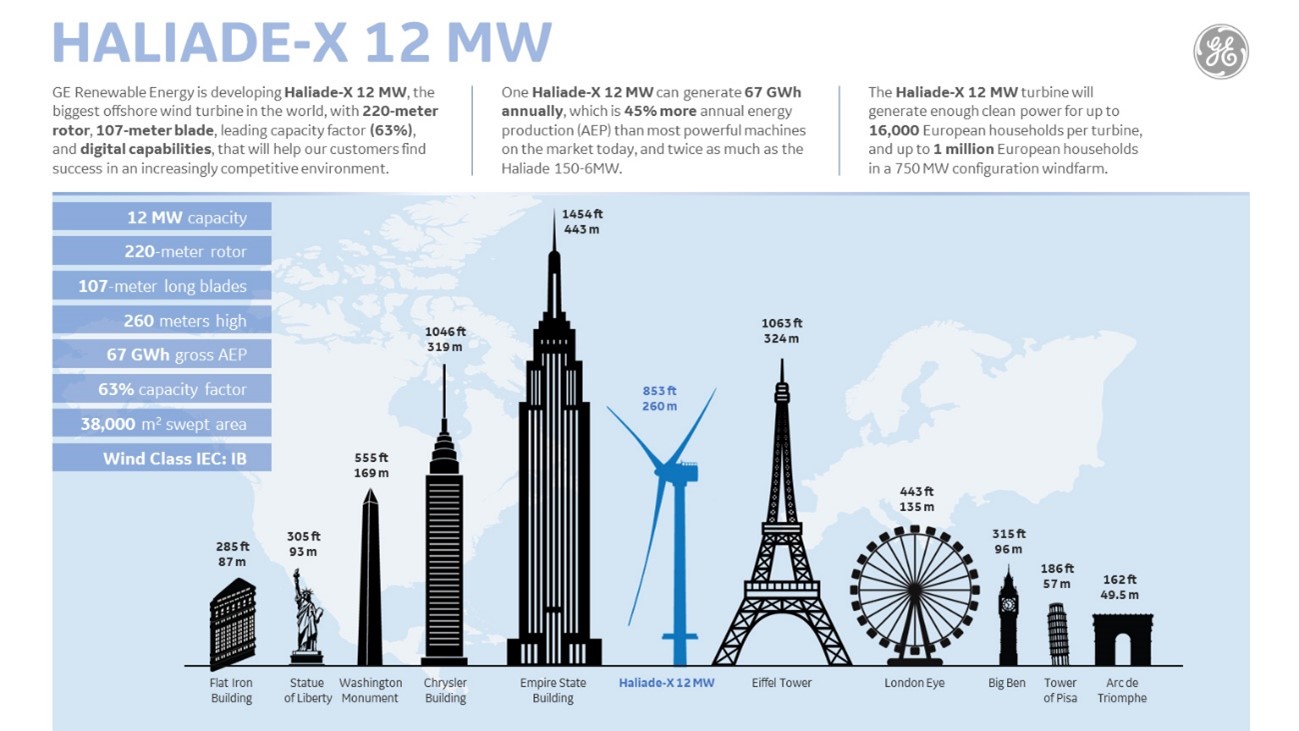
Capacity Growth: Modern turbines now exceed 15 MW per unit, making offshore wind farms with fewer turbines capable of producing massive amounts of electricity.
Height Matters: By reaching higher altitudes, turbines can harness stronger, more consistent winds. Taller towers—often exceeding 150 meters—are becoming standard.
-
Aerodynamic Innovations
Adaptive Blades: New blade designs incorporate sensors and actuators that adjust their angle in real time to maximize efficiency and reduce stress during turbulent winds. Advanced blade designs reduce drag and maximize lift, allowing turbines to operate efficiently across a wider range of wind conditions.
Bio-Inspired Designs: Engineers take inspiration from nature, such as mimicking humpback whale fins (tubercles) to create blades with better lift and reduced drag.

Low-Noise Designs: Special blade shapes reduce the noise caused by cutting through the air, making turbines more acceptable in areas near human settlements.
Variable-Speed Turbines: By adjusting rotor speed to match wind conditions, these turbines optimize energy output.
-
Vertical Axis and Niche Turbines
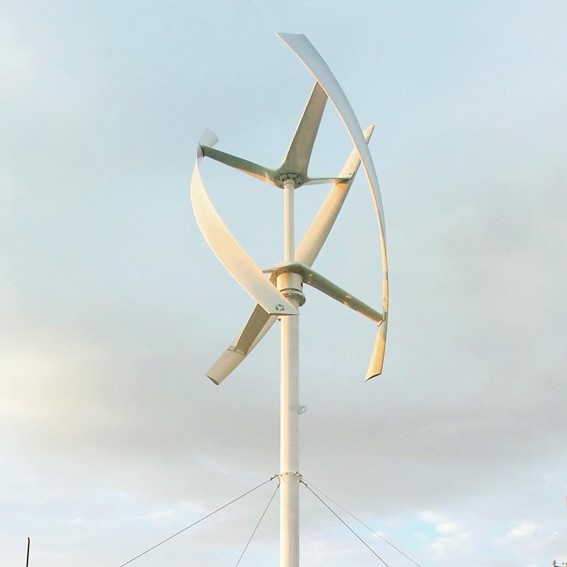
- Vertical Axis Turbines: These are compact and can function in urban environments where wind directions vary. Their smaller footprint makes them ideal for rooftops or tight spaces.
- Micro and Mini Turbines: Smaller turbines, designed for individual homes or small businesses, are gaining popularity as a part of decentralized energy systems.

-
Material Advancements
Lightweight and Durable Materials: Fiberglass and carbon fiber composites reduce the overall weight of turbines while maintaining structural integrity without compromising durability. Lighter blades are easier to install and less demanding on the supporting structures.
Recyclable Components: Teams of engineers are working on fully recyclable blades to minimize waste. This innovation aligns with circular economy goals. Innovations in turbine blade recycling address environmental concerns, helping to reduce waste at the end of their lifecycle.
-
Digital Technology Integration
Smart Technology and Automation
Digital Twins: Virtual models of wind turbines allow engineers to monitor performance and predict maintenance needs without physical inspections.
Real-Time Monitoring: Wind turbines are now equipped with sensors that monitor performance, weather conditions, and mechanical health in real time. This data improves maintenance and extends turbine lifespans. Smart Sensors and IoT enabled sensors measure vibration, temperature, wind speed, and other parameters. These insights help prevent breakdowns and optimize turbine performance.
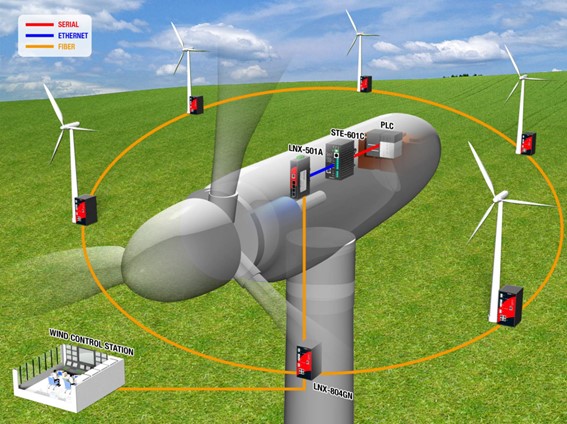
Drones and Robots for Maintenance: Drones equipped with cameras and AI perform detailed inspections of turbine blades, identifying cracks or wear. Robots are also being developed to clean and repair blades autonomously.
AI and Machine Learning: Predictive analytics optimize turbine performance and reduce downtime, ensuring consistent energy generation.
- Offshore Wind Turbines
- Floating Wind Turbines: Innovations in floating turbine platforms allow deployment in deep waters where wind speeds are higher and more consistent, significantly expanding the potential for offshore wind energy. Platforms like TetraSpar and WindFloat enable turbines to be installed in waters deeper than 60 meters. These floating structures are tethered to the seabed, allowing them to be placed in previously inaccessible areas.

- Hurricane-Resistant Designs: Offshore turbines are now being engineered to withstand extreme weather conditions, including Category 5 hurricanes.
- Integration with Aquaculture: Some offshore wind farms are being combined with fish farming or seaweed cultivation, maximizing the use of marine spaces.
- Large-Scale Offshore Farms: Offshore farms can generate gigawatts of power, contributing to global energy grids and helping nations meet their renewable energy targets.
-
Scalability and Cost Reduction
- Economies of Scale: Larger turbines with higher capacities reduce the cost per kilowatt-hour, making wind energy more competitive with fossil fuels.
- Modular Designs: Simplified assembly and installation processes reduce construction costs and make turbines easier to deploy in remote areas.
-
Hybrid and Innovative Designs
Hybrid Systems: Turbines integrated with solar panels or energy storage systems create hybrid solutions, ensuring a steady power supply even during low-wind periods.
Vertical Axis Turbines: These turbines, which differ from traditional horizontal-axis designs, are being developed for urban and niche applications due to their compact size and ability to harness wind from all directions.

-
Grid Integration and Energy Storage
Smarter Grids: Advances in turbine technology are complemented by improved grid infrastructure that manages intermittent wind energy effectively. These systems dynamically balance energy demand and supply, integrating wind power seamlessly with other renewable sources.
Battery Innovations: Coupling turbines with large-scale lithium-ion or flow batteries ensures continuous power supply, even during lulls in wind.
Battery Storage: Pairing wind turbines with large-scale batteries ensures energy availability during periods of low wind, improving reliability.

-
Environmental and Community Impact
Green Hydrogen Production: Excess electricity generated by wind farms is being used to produce hydrogen, which can be stored and transported as an alternative energy source.
Reducing Land Use: Larger turbines mean fewer installations are needed, minimizing the environmental impact on land and wildlife habitats.
Noise and Aesthetic Improvements: Engineers are designing quieter and visually less intrusive turbines to address public concerns and boost adoption in communities.
Future of Wind Energy
- Airborne Wind Energy: Innovations like kite-based or drone-based wind systems harness high-altitude winds with smaller infrastructures.
- Hybrid Systems: Combining wind turbines with solar panels, geothermal systems, or even hydroelectric facilities to create all-weather renewable solutions.
- Next-Generation Blades: 3D printing and modular blade systems could allow for quicker manufacturing and on-site assembly.
- Sustainability Goals: Net-zero carbon emissions in turbine production and end-of-life recycling will make wind energy even greener.
Impacts Of Advanced Wind Turbine Designs On The Future Of Renewable Energy
- Energy Access for All: Advanced wind turbine designs are bringing renewable energy to remote areas, islands, and off-grid communities.
- Economic Benefits: Wind energy creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance while reducing dependency on imported fossil fuels.
- Climate Goals: As countries set aggressive decarbonization targets, wind energy is poised to play a central role in achieving net-zero emissions.
Conclusion
Wind turbines stand as a testament to human ingenuity and our commitment to finding sustainable solutions to our energy needs. With wind energy playing an ever-expanding role in the global energy mix, we are taking strides toward a cleaner and greener future. The efforts of wind turbine technicians, bravely climbing to great heights, are helping to drive this transformation. As we continue to harness the power of the wind, we move closer to securing a healthier planet for generations to come.
Access various online courses. Our programs, tailored for working professionals, offer a flexible path to advance your studies while managing your current job.
Join Ken Institute and unlock a world of online courses in Occupational Health and Safety, Fire Safety, and Environment and Sustainability and Mechanical Engineering. Propel your career to new heights.
Get in touch with us at: info@keninstitute.com
Visit our website: www.keninstitute.com
Call us on +917569034271
Let’s connect together on: Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, and Instagram.

