“The Green Hydrogen Projects in Oman and Egypt” are rapidly advancing with large-scale, integrated mechanical systems driving major breakthroughs in renewable hydrogen and ammonia production featuring combinations of renewable energy sources, advanced electrolyzers, battery storage, and hydrogen storage, representing some of the most ambitious energy transitions in the region.
Oman favors alkaline for proven reliability at scale and cost but may add PEM for advanced, modular units in expansion.
Egypt adopts PEM for agile pilot projects and plans a mix with alkaline as megawatt-scale systems expand.
Both countries prioritize electrolyzers’ efficiency, scalability, and integration with renewables, with ongoing upgrades as global technology matures.
Key Mechanical Systems in Green Hydrogen Production
These mechanical systems are revolutionizing the energy sector in both countries by enabling large-scale, carbon-neutral fuel production, shifting economic reliance away from traditional oil and gas exports.
Renewable Energy Infrastructure: Both nations leverage their abundant solar and wind resources. The mechanical systems involved here include vast arrays of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels with associated mounting and tracking systems, and large wind turbines.
Water Treatment and Desalination: Green hydrogen production requires a consistent supply of pure water. Given the coastal locations of many projects, large-scale desalination units and associated pumps, piping, and filtration systems are essential mechanical components for processing seawater into the required high-purity water feedstock.
Electrolysis Stacks: At the heart of the process are the electrolyzers, primarily Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) or Alkaline types, which are technically complex mechanical assemblies designed to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. This process involves precise fluid dynamics, temperature control, and material science to handle the process at typical operating temperatures (60–120 °C).

Image Source: certrec
Gas Compression Systems: Once produced, hydrogen gas is compressed to high pressures (up to 30-200 bar for storage or further processing) to enhance storage density and facilitate transportation. This requires powerful industrial compressors and a robust network of high-pressure pipelines, valves, and fittings, which are critical mechanical engineering components.
Ammonia Synthesis Plants: Many projects in Oman and Egypt aim to convert the produced green hydrogen into green ammonia for easier and more efficient export via maritime transport. This conversion utilizes the energy-intensive Haber-Bosch (HB) process, which involves significant mechanical systems such as air separation units (to produce nitrogen), high-temperature catalytic reactors, heat exchangers, and further compression and cooling equipment.
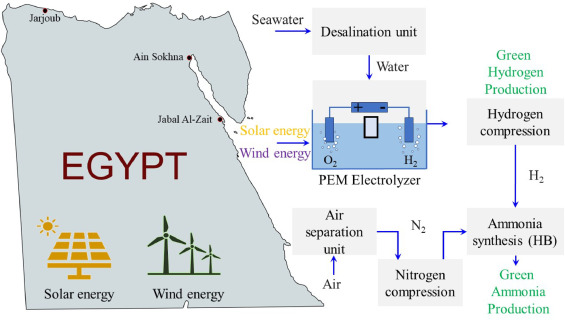
Image Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/
Storage and Transport Infrastructure: This includes large, often cryogenic, hydrogen storage vessels and tanks, as well as specialized infrastructure for liquefaction or loading onto innovative zero-boil-off maritime transport vessels. High-pressure hydrogen storage vessels, enable robust supply for refueling stations and industrial use, with vessels rated up to 1034 bar for safety and daily throughput.
Battery Energy Storage: Integrated battery energy storage smooths renewable fluctuations and provides continuous electrolysis operation.
Pipelines and Conversion: Produced hydrogen is transported to conversion plants for synthesis into ammonia (over 1 million tonnes per year), leveraging Oman’s port and industrial zones for export.
Multi-Energy Refueling: Projects also integrate hydrogen with EV charging and conventional fueling, showcasing modern multi-energy hubs.
Advanced Control Systems: Front-End Engineering Design (FEED) studies include automated control and optimization for efficient hydrogen, ammonia, and renewable integration.
International Collaboration: Technology providers and engineering firms are transferring expertise and mechanical innovations from established projects in Oman to new Egyptian plants.
Key Innovations and Impact
Both countries are setting new global benchmarks for sustainable mechanical engineering, leveraging cutting-edge systems to revolutionize how hydrogen is produced, stored, and exported.
- Integration of wind, solar, battery storage, and electrolyzer technology achieves continuous, scalable hydrogen production across harsh climates.
- High-pressure hydrogen storage systems and pipelines secure safe, reliable transport and refueling, essential for local industrial adoption and export capacity.
- Mega-scale mechanical deployment supports regional energy transition, job creation, and cross-border technology transfer.
These advances are pivotal for shifting to decarbonized industrial energy and transforming international supply chains.
Top 10 Upcoming Green Hydrogen Projects in Oman (2025)
Oman aims to gain prominence in the global hydrogen industry among other nations. Oman’s green hydrogen projects are helping the country progress towards its goal of Oman Vision 2040, that aims to promote local renewable energy sources and achieve zero carbon emissions by 2050.
To support Oman’s energy development, an initiative of Hydrogen Oman SPC (Hydrom) was established in 2022 under Salim Nasser AL Aufi – Minister of Energy and Minerals in Oman.
Top Upcoming Green Hydrogen Projects in Oman (By Capacity)
These green hydrogen projects in Oman primarily revolve around large-scale, government-backed initiatives with significant international partnerships. Major projects in Oman utilize large-scale alkaline electrolyzers, supplied by Sungrow Hydrogen, designed for multi-MW installations and robust integration with vast solar and wind power.
- Green Energy Oman (GEO) — A 1.8 GW project involving Shell, EnerTech, OQ, and InterContinental Energy, expected to produce about 1.8 million tonnes of green hydrogen per year. It uses 4 GW renewable energy initially, expandable to 25 GW.
- HyPort Duqm — A joint venture with DEME and BP, with 1.3 GW renewable energy capacity in phases, aiming for large-scale green ammonia production. Phase 1 produces 330,000 tonnes and Phase 2 650,000 tonnes of green ammonia.
- SalalaH2 — A consortium including OQ, Marubeni, Samsung C&T, Dutco, expected to produce 1,000 tonnes of green ammonia daily, powered by 1 GW of renewables and 400 MW electrolyzers.
- POSCO-ENGIE Green Hydrogen Project — A 200 ktpa green hydrogen facility with construction starting in 2027, leveraging wind and solar power.
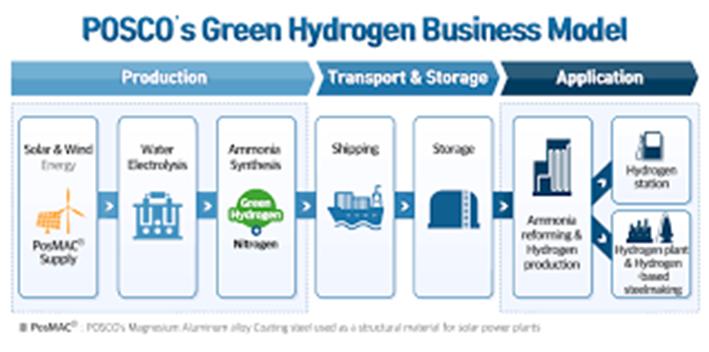
Image Source: newsroom.posco
- Amnah Green Hydrogen Project — Backed by Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners and others, planned to produce 200 ktpa.
- Actis and Fortescue Green Hydrogen Project — Up to 200 ktpa, powered by 4.5 GW wind and solar energy, aimed at local and export markets via Salalah port.
- EDF Group, J-POWER, Yamna Project — Targeting 178 ktpa green hydrogen by 2030 with 4.5 GW of renewable energy, supplying green ammonia production.
- Sur Hydrogen Cluster — A consortium with Oman LNG, Sultan Qaboos University, OQ, and others studying a 177.755 MW green hydrogen feasibility project.
- ACME Duqm Hydrogen Project Phase 2 — Estimated 497 ktpa production using solar, scheduled around 2028.
- Fortescue Future Industries Oman Hydrogen Project — A joint venture targeting 200 ktpa by 2030.
“These projects are concentrated mainly in the Duqm and Salalah regions, leveraging Oman’s strong wind and solar resources. The projects are key parts of Oman’s national hydrogen strategy aiming for 1 to 1.5 million tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2030.”
Top 10 Upcoming Green Hydrogen Projects in Egypt
These projects encompass large-scale renewable energy use (solar, wind) to produce green hydrogen and ammonia, positioning Egypt as a major green hydrogen hub targeting European and global markets. Egypt’s pilot and flagship green hydrogen projects deploy a mix of PEM and alkaline electrolyzers.
- Egypt Green Hydrogen Project (Ain Sokhna, Suez Canal Economic Zone)
Consortium: Scatec, Fertiglobe, Orascom Construction, Sovereign Fund of Egypt.
Capacity: 100 MW electrolyser, ~13,000 tonnes of H2/year, 74,000 tonnes renewable ammonia/year.
Operational start: Expected ammonia exports from 2027, scaling to 397,000 tonnes by 2033

Image Source: egypttoday
- BP, Masdar, Hassan Allam Utilities & Infinity Power Consortium (Sokhna Integrated Zone)
Investment: €13.5 billion
Pilot phase capacity: 330,000 tonnes/year by Q4 2030
Phase 1 capacity: 2.5 million tonnes/year by Q4 2032
- Ocior Energy Holding (UAE-based, Sokhna Integrated Zone)
Investment: €3.9 billion
Pilot phase: 100,000 tonnes/year by Q4 2029
Phase 1: 900,000 tonnes/year by Q4 2031
- TAQA Arabia (Egypt) and Voltalia (France) Consortium (Sokhna Integrated Zone)
Investment: €3.8 billion
Pilot & Phase 1: 355,700 tonnes/year by Q4 2030 and 2032 respectively

Image Source: solarquarter
- DAI Infrastruktur (Germany) (East Port Said Integrated Zone)
Investment: €10.2 billion
Phase: 7 million tonnes/year by Q4 2028
- $17 Billion Mega Green Hydrogen Plant in South Sinai by Egyptian Ministry
Capacity: 3.1 GW solar-powered electrolyser plant
Annual production: 400,000 tons liquefied hydrogen
Phases finishing 2030, 2033, 2035
- Framework Agreement – Voltalia and TAQA Arabia for 1 GW project in Suez Canal Zone
Investment: US$3.4 billion
Target operational date: Around 2030
- HYPORT Gargoub Project (Western Desert)
Three-phase project
Phase 1 goal: 320,000 tonnes green ammonia/year
- Globeleq SCZONE Hydrogen Project Phase 2
Capacity: 1.945 million tonnes/year capacity
Operational by 2028
- ACME Group Sokhna Hydrogen Project Phase 2
Capacity: 2.1 million tonnes/year
Operational start planned 2030
“The Suez Canal Economic Zone and South Sinai are key hubs for these developments. Investments range from several billion to over ten billion euros/dollars, reflecting strategic importance. “
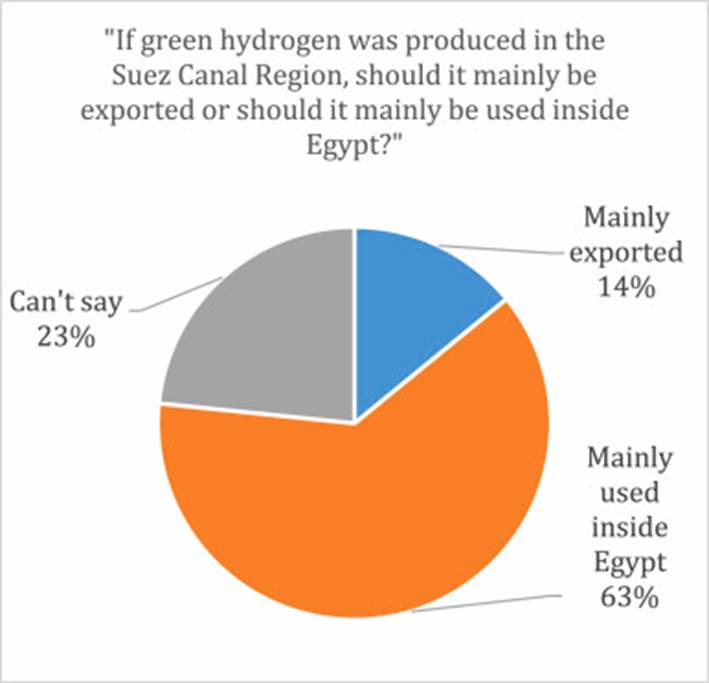
Image Source: sciencedirect
Supply Chain Risks Affect Electrolyser Deployment in Oman and Egypt
Electrolyzer deployment in the GCC and North Africa, including Oman and Egypt, faces several notable supply chain risks that affect project scalability, cost, and reliability.
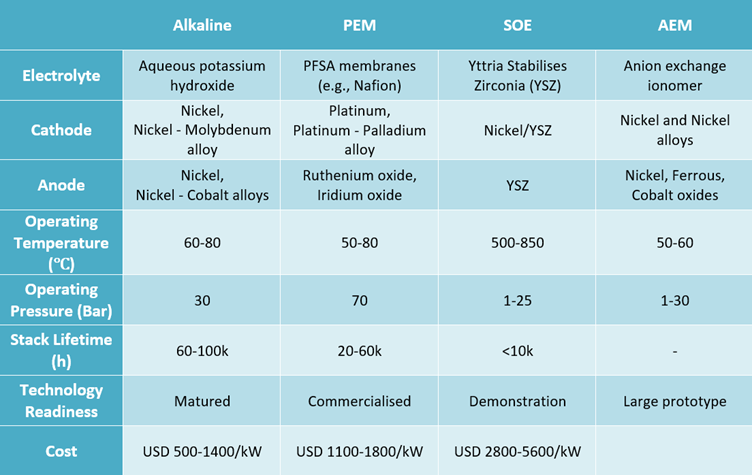
Image Source: ceew
- Critical Material Constraints
Electrolyzers, especially PEM types, require platinum-group metals such as iridium and platinum, while alkaline units rely on nickel and potash.
These materials are in high demand globally for other industries, and supply is concentrated among a few major suppliers, exposing projects to price volatility and potential shortages.
- Manufacturing Bottlenecks and Fragmented Supply Chains
Global electrolyzer manufacturing is currently insufficient to meet projected demand, with less than 20% of the required capacity in place for 2030 targets.
Most large-scale manufacturing requiring long import logistics, transportation risks, and geopolitical uncertainties. Fragmented supply chains, with components sourced from multiple suppliers, create coordination issues and reduce scalability.
Infrastructure and Logistics
Insufficient port, storage, and transport infrastructure for hydrogen distribution, storage, and integration with renewables delays implementation and increases up-front costs.
Water Supply and Energy Dependence
Electrolyzers require large volumes of purified water, while many projects are in water-scarce areas, necessitating investment in desalination or water recycling.
- Financial and Market Uncertainties
Fluctuating capital and operational costs, exacerbated by raw material price swings and global inflation, weak demand for green hydrogen or its derivatives, coupled with uncertain offtake agreements, increase project risk and complicate investment planning.
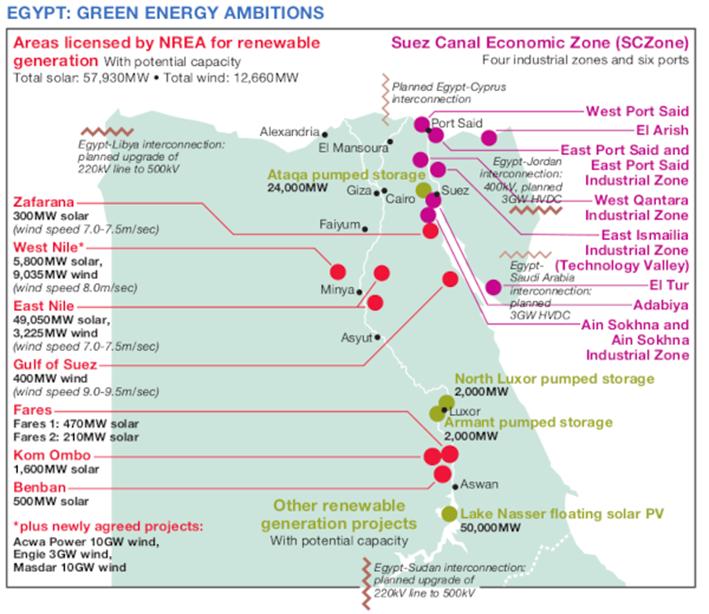
Image Source: africa-energy
Policy to Reduce Dependence on Pgms
Recycling can significantly reduce dependence on iridium and platinum group metals (PGMs) by recovering these precious metals from end-of-life products and industrial waste, creating a circular supply chain that lessens reliance on primary mining.
A robust PGM recycling infrastructure, supported by regulatory incentives and technology investment, is essential for securing green hydrogen electrolyzer supply chains and achieving long-term industrial sustainability goals.
Current and Future Scope of the Green Hydrogen Industry in Oman
The green hydrogen industry in Oman is expanding with several initiatives under the Oman Vision 2040 to position the Sultanate of Oman on the pedestal of the global green hydrogen sector. Oman’s government aims to produce 1 million metric tons of clean hydrogen annually by the end of 2030. Additionally, under this program, Oman aims to achieve 30 GW of electrolyzer capacity by 2040.
Current and Future Scope of the Green Hydrogen Industry in Egypt
Egypt has significant current and future potential for green hydrogen due to its abundant solar and wind resources, government incentives, and strategic location. The country aims to become a major producer and exporter, particularly to Europe, with targets for large-scale production and billions in anticipated investments. The government has implemented a law with incentives like tax concessions to attract investment for green hydrogen projects.
Egypt aims to produce 5.6 million tonnes of green hydrogen and ammonia annually by 2040 under a “green scenario”. A major focus is on exporting green hydrogen and its derivatives to meet global demand, particularly from Europe.
By scaling up green hydrogen, Egypt aims to decarbonize its economy, aligning with its national development strategy, Egypt’s Vision 2030, which targets 42% renewable energy by 2030.
Image Source: sciencedirect
End Lines
The Green Hydrogen Projects in Oman and Egypt” rely on a common suite of sophisticated mechanical systems that form the core of the hydrogen production, processing, storage, and transport value chain. These systems integrate renewable energy capture, water electrolysis, and large-scale compression and synthesis units.
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““
Join us and unlock a world of online courses in Mechanical Engineering, Occupational Health and Safety, Fire Safety, and Environment and Sustainability. Propel your career to new heights.
Propel your career to new heights.
Connect now and take the next step toward professional excellence!
+91 7569034271
Let’s connect together on: Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, and Instagram.


