Under the Qatar National Vision 2030, Qatar’s implementation of smart waste management, utilizing IoT(Internet of Things) bins and AI routing, plays a significant role in achieving its sustainability objectives. Traditional waste management systems often lead to inefficient collection routes and overflowing bins. IoT technology addresses waste collection efficiency and promotes environmental stewardship.
Qatar’s waste management landscape in 2026 is characterized by a “Smart City” revolution driven under the Qatar National Vision 2030.
This technological shift utilizes IoT-enabled bins and AI-driven routing to improve operational efficiency and advance national sustainability goals.
Innovative Waste Management Technologies in Qatar
Qatar’s initiatives target 38% recycling from current 8%, prioritizing reduction, reuse, recovery, and minimal landfilling per the waste hierarchy. Facilities like waste transfer stations and the Domestic Solid Waste Management Centre enable sorting, composting, and energy recovery, reducing landfill reliance. The Zero Waste campaign fosters community awareness and investment for circular economy goal.
8 Jul 2024 — Qatar is setting a benchmark for sustainable waste management in the region. This includes smart garbage bins, waste-to- Green Planet Solutions.
Mannai InfoTech Wins Prestigious Qatar Digital Business Award 2024 for Best Smart Solution
Technology is Used to Reduce Waste by Okon Recycling
Core Technologies in 2026
IoT-Enabled Smart Bins
Equipped with ultrasonic sensors to monitor fill levels in real-time.
Automatically alert collection teams when reaching capacity, preventing overflows and reducing unnecessary trips.
In pilot areas like Al Wakrah, the system monitors over 7,500 tracked containers.
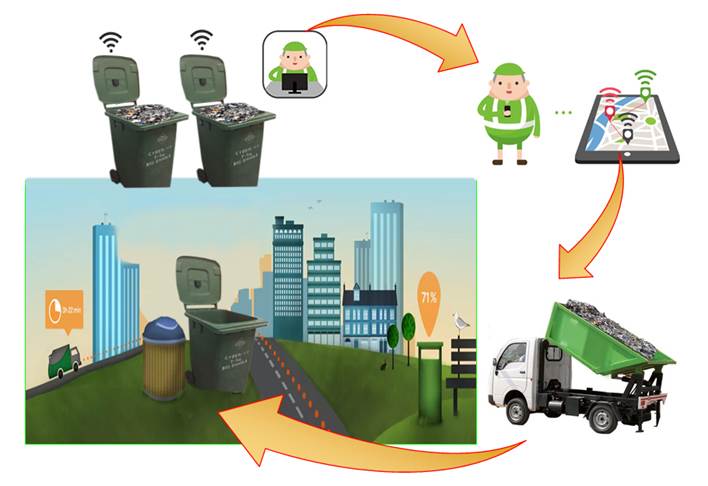
Image Source: smartworlds
IoT technology to revolutionize implementation of smart bins in Qatar:
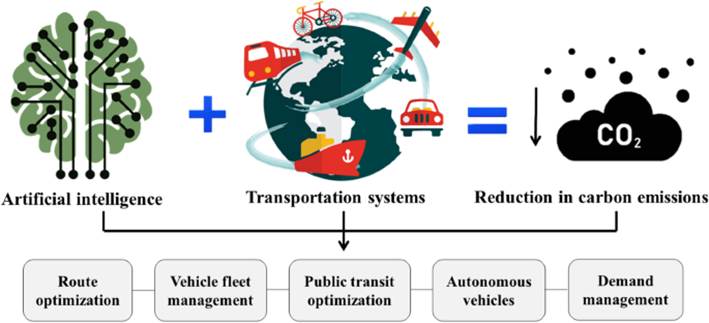
AI Route Optimization:
Uses real-time data on bin levels, traffic, and vehicle location to map the most efficient collection paths.
AI-powered systems have shown potential to improve collection efficiency by up to 25% and reduce fuel consumption by over 15%.

Image Source: factual-consulting
AI-Powered Sorting:
Robotic systems and computer vision are being integrated at sorting stations to identify and separate recyclables (paper, metal, plastic) with high accuracy, reducing human error and contamination.
Sustainability & Economic Impact
Reduced Emissions: Smart routing eliminates “static” schedules, significantly lowering carbon emissions from fleet operations and preventing environmental hazards from decomposing waste.
Circular Economy Goals: Qatar aims to recycle 95% of waste by 2030. The current roadmap includes increasing landfill diversion through AI-enhanced material recovery.
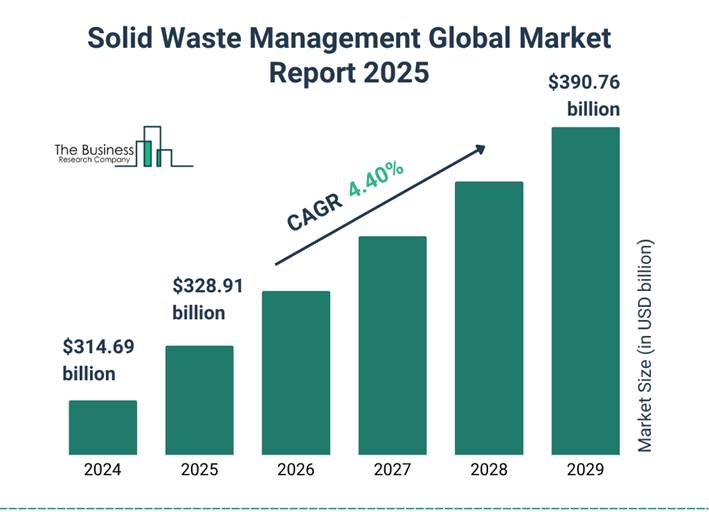
Market Growth: The waste management market in Qatar is projected to grow to approximately $548.47 million in 2025 and continue expanding through 2026, supported by over QAR 1.2 billion (approx. $330M) in government sustainability investments.
Resource Recovery: New facilities, such as the Al-Afjah recycling hub, are designed to process specialized streams like e-waste and construction debris using advanced tracking.
Strategic Implementation
The revolution is part of the TASMU Smart Qatar program and the Ministry’s 2024–2030 strategy, focusing on digital transform to enhance the quality of life in cities like Doha, Lusail, and Al Rayyan.
Contamination Detection: Advanced sensors can also detect if the wrong type of waste has been deposited, helping to improve recycling purity rates.
Efficiency: This data eliminates unnecessary collection trips, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs.
AI and Machine Learning for Optimal Routing
The data gathered from the IoT bins is processed using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms.
Dynamic Route Optimization: Instead of following fixed schedules, collection vehicles receive optimized routes daily, ensuring only full or nearly full bins are serviced.
Reduced Carbon Footprint: This optimization significantly decreases vehicle mileage, directly contributing to a lower carbon footprint and better air quality in the country.
Support for Sustainability Goals
This technological shift aligns with Qatar’s broader environmental goals of the Qatar National Vision 2030.
Resource Management: By optimizing waste collection, the system improves overall resource management and minimizes landfill usage.
Promoting Recycling: Smarter monitoring and contamination detection support initiatives for better waste separation and higher recycling rates.
Data-Driven Policy Making: The robust data collected from the smart system enables the government to make informed decisions and develop more effective future waste management policies.
The Costs of Implementing Smart Bins in Doha
The available data from Qatar-focused IoT providers and global analogs indicate initial hardware and setup expenses range from QAR 5,000–10,000 per advanced sensor-equipped bin, scaling with volume for city-wide deployment. Providers like IoT Shabaka and Convexicon emphasize RFID tagging, GPS integration, and cloud platforms without exact Doha figures, while general savings post-implementation include 40% fuel cost reductions yielding 5 million QAR annual benefits per district. Qatar’s solid waste market, valued at USD 2.73 billion in 2025, absorbs these investments through efficiency gains aligning with smart city initiatives.
Per-Bin Cost Components
Ultrasonic fill sensors, LoRaWAN connectivity, tamper/fire detection: ~USD 200–500 (QAR 730–1,830) per unit, with 5+ year battery life.
Installation (GIS mapping, RFID tagging, vehicle readers): QAR 1,000–2,000 per bin, including field teams.
Software platform (real-time dashboard, AI routing):
Subscription-based, often bundled at USD 500–1,000/month per district.
ROI and Funding
Payback occurs within 1–2 years via 30–40% operational savings, 50% carbon reduction, and 80% fewer overflows, funded by Ashghal or PPPs in Qatar’s USD 3.88 billion market by 2030. High upfront costs challenge adoption, but pilots in Doha demonstrate viability through transparent monitoring and SLA adherence.
AI Routing: Fuel and Emissions Reduction Metrics
AI routing in waste management analyzes real-time data from IoT bins, traffic, and vehicle telemetry to compute optimal paths, slashing unnecessary detours and idle time that drive up fuel use and emissions.
Fuel Reduction Metrics
Dynamic algorithms cut total distance traveled by 10-20%, directly lowering fuel consumption by 11.6% on average per studies on residential collections. Fewer trips and balanced loads prevent overloads, yielding 30-40% operational savings including diesel costs, as seen in Qatar-linked pilots. Real-time reoptimization adapts to delays, maintaining efficiency.
Emissions Impact
Shorter routes and efficient packing reduce CO2 emissions by 15-25%, aligning with sustainability targets through minimized engine idling and acceleration cycles. In dynamic models, vehicles cover 20-30% less distance than static plans, proportionally cutting GHG output while handling equivalent waste volumes. Qatar deployments report 50% carbon drops via integrated AI platforms.
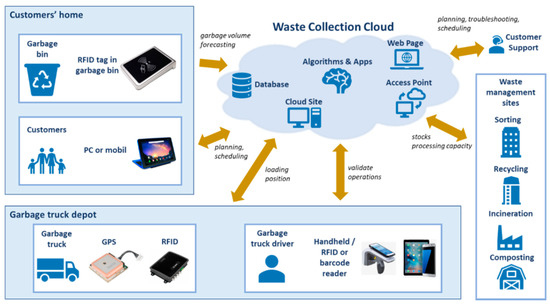
Image Source: mdpi
Governing Regulations for Smart Waste Systems In Qatar
Qatar’s smart waste systems fall under the oversight of the Ministry of Municipality (MoM), guided by overarching environmental and waste management laws. These regulations emphasize integrated waste hierarchy, technology adoption for efficiency, and sustainability alignment with Qatar National Vision 2030.
Core Regulations
Law No. 30 of 2002 (Environmental Protection Law): Prohibits illegal dumping, mandates proper treatment/disposal, and sets standards for waste handling including smart tech integration to minimize environmental harm.
Ministerial Decision No. 143 of 2022: Targets plastic waste reduction, indirectly supporting smart segregation sensors in bins for compliance.
Waste Hierarchy Policy (NDS 2011-2016, ongoing): Prioritizes prevention, reuse, recycling, recovery over landfilling; requires smart systems like IoT bins for monitoring and AI routing to achieve 38% recycling target.
Implementation Standards
Ashghal and MoM enforce tech pilots (e.g., underground smart containers) via public cleanliness departments, with PPP models for privatization of transfer stations. New 2025 segregation rules mandate household separation, bolstered by IoT for enforcement and data tracking. Facilities like DSWMC must meet energy recovery and emission controls under these frameworks.

Image Source: iloveqatar
Summary
In 2026, Qatar’s waste management landscape is characterized by a “Smart City” revolution driven by the Ministry of Municipality under the Qatar National Vision 2030 strategy. This technological shift utilizes IoT-enabled bins and AI-driven routing to improve operational efficiency and advance national sustainability goal.
Qatar employs IoT-enabled smart bins and AI-optimized routing to modernize waste collection, addressing urban growth challenges while advancing national sustainability targets. These technologies enhance efficiency, cut emissions, and boost recycling in line with Qatar National Vision 2030. Implementation spans Doha, Lusail, and other areas through public-private partnerships.
**********************************************************************************
Join Us!
Join us and unlock a world of online courses in Mechanical Engineering, Occupational Health and Safety, Fire Safety, and Environment and Sustainability. Propel your career to new heights.
Propel your career to new heights.
Connect now and take the next step toward professional excellence!
+91 7569034271
Let’s connect together on: Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, and Instagram.


