Mechanical engineering is a broad field that encompasses various disciplines and skills. To continuously stay updated and also for a successful career in the field, “Mechanical Engineer Should Know” about advancements in technology, industry trends, and emerging fields within mechanical engineering. The field of mechanical engineering is diverse, and individual career paths may emphasize different aspects based on specialization or industry focus.
Mechanical engineer should know that staying curious, open to learning, and adaptable to new technologies are key attributes for a successful career.
Here are some interesting and important things that every mechanical engineer studies in the institutes:
Thermodynamics: Understanding the principles of heat and energy transfer is crucial for designing and analyzing mechanical systems, engines, and processes.
Fluid Mechanics: Knowledge of how fluids behave is essential for designing pumps, turbines, and other fluid systems.
Mechanics of Materials: Understanding how different materials respond to stress and strain is crucial for designing durable and safe structures and components.
Machine Design: Learning about the principles of designing machines and mechanical systems, including gears, bearings, and mechanisms.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design): Proficiency in using CAD software for designing and modeling mechanical components and systems.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA): The ability to use FEA tools to simulate and analyze the structural integrity and performance of designs before they are physically built. FEA is a computational technique used to analyze how structures and components behave under different conditions.
FEA is crucial for predicting the stress, strain, and deformation of mechanical parts, ensuring that designs are structurally sound and meet safety requirements before physical prototypes are built.
Manufacturing Processes: Knowledge of various manufacturing techniques such as machining, casting, welding, and 3D printing is essential for translating design concepts into physical products.
Control Systems: Understanding feedback control systems is important for designing automated systems and robotics. This includes feedback mechanisms to maintain desired outputs and adjust for variations.

Control systems are used in designing automated systems, robotics, and machinery to ensure stability, accuracy, and optimal performance.
Skills: Mechanical engineers should know about classical control theory, modern control techniques, and programming languages (like MATLAB or Python) for control algorithm implementation.
Materials Science: Knowledge of different materials and their properties, helping in material selection for specific applications.
Project Management: Skills in managing projects, including budgeting, scheduling, and coordinating team members.
Renewable Energy: Awareness of sustainable and renewable energy technologies, such as wind, solar, and hydropower. Mechanical engineers can be involved in designing and optimizing renewable energy systems by understanding the principles of energy conversion, knowledge of energy storage systems, and familiarity with renewable energy technologies.
Robotics: Understanding the principles of robotics and automation, including programming and control.
Biomechanics: Knowledge of mechanics as it applies to the human body, useful in fields like medical devices and prosthetics.
Environmental Impact: Consideration of the environmental impact of designs and processes, incorporating principles of sustainability.
Patents and Intellectual Property: Mechanical engineers should know the basics of intellectual property law and patents to protect innovative designs and ideas.

Communication Skills: Effective communication, both written and verbal, is crucial for collaborating with interdisciplinary teams and presenting ideas to stakeholders.
Ethics: Awareness of ethical considerations in engineering, including safety, social impact, and responsible innovation.
The Additional Areas of Knowledge And Skills That Can Be Beneficial For Mechanical Engineers:
-
Lean Manufacturing:
Understanding lean principles and techniques for optimizing production processes and minimizing waste.
Description: Lean principles aim to optimize efficiency by eliminating waste, improving processes, and enhancing value for the customer.
Application: In manufacturing settings, lean principles help streamline production, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity.
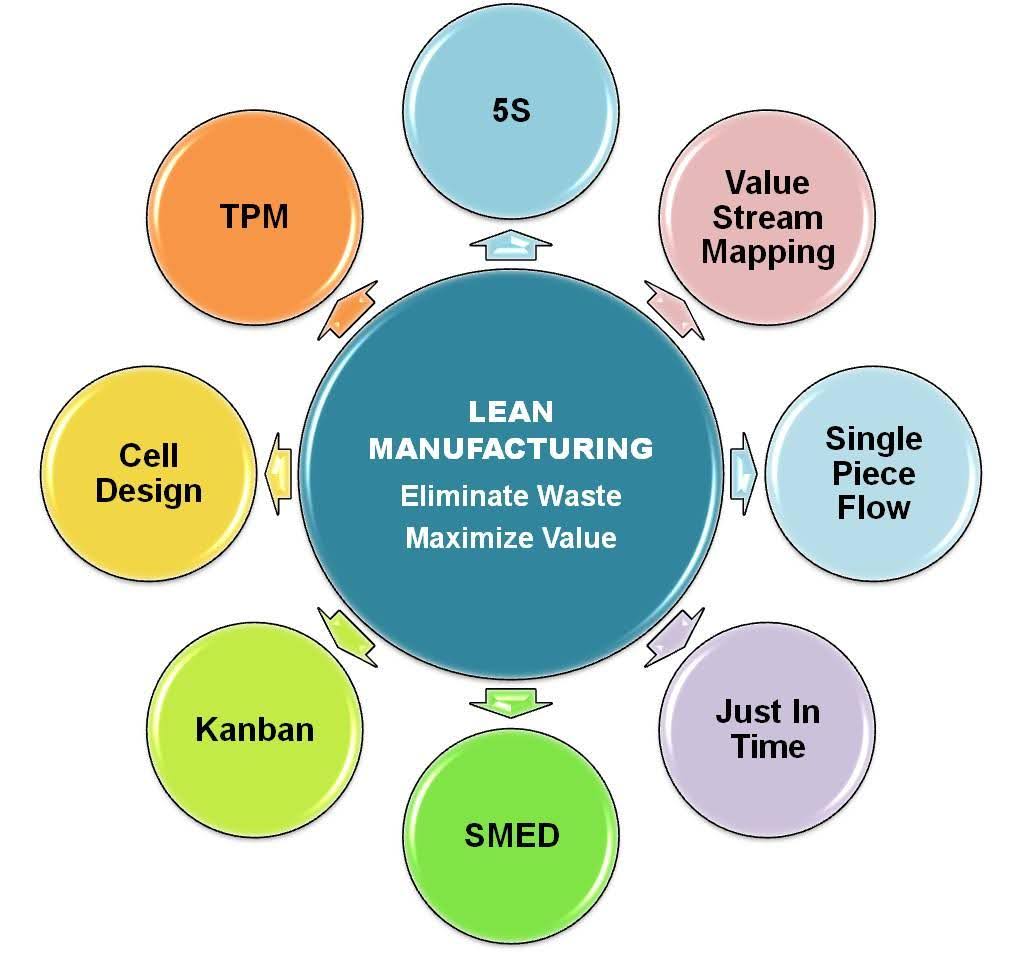
Tools: Techniques like 5S (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain), Kanban, and value stream mapping are commonly used in lean manufacturing.
-
HVAC Systems:
Mechanical engineers should know the techniques of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, especially in the context of energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
Description: HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It involves designing systems that control the temperature, humidity, and air quality in buildings.
Application: Mechanical engineers working on HVAC systems ensure that buildings are comfortable, energy-efficient, and comply with environmental standards.
Skills: Understanding thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and knowledge of HVAC equipment and control systems.
-
CAD/CAM Integration:
Mechanical engineers should know the process of Integrating Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) with CAD for seamless design-to-manufacturing processes.
Description: CAD (Computer-Aided Design) is used for creating 3D models, while CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) involves using computers to control machine tools for manufacturing.
Application: Integration ensures seamless communication between the design and manufacturing processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
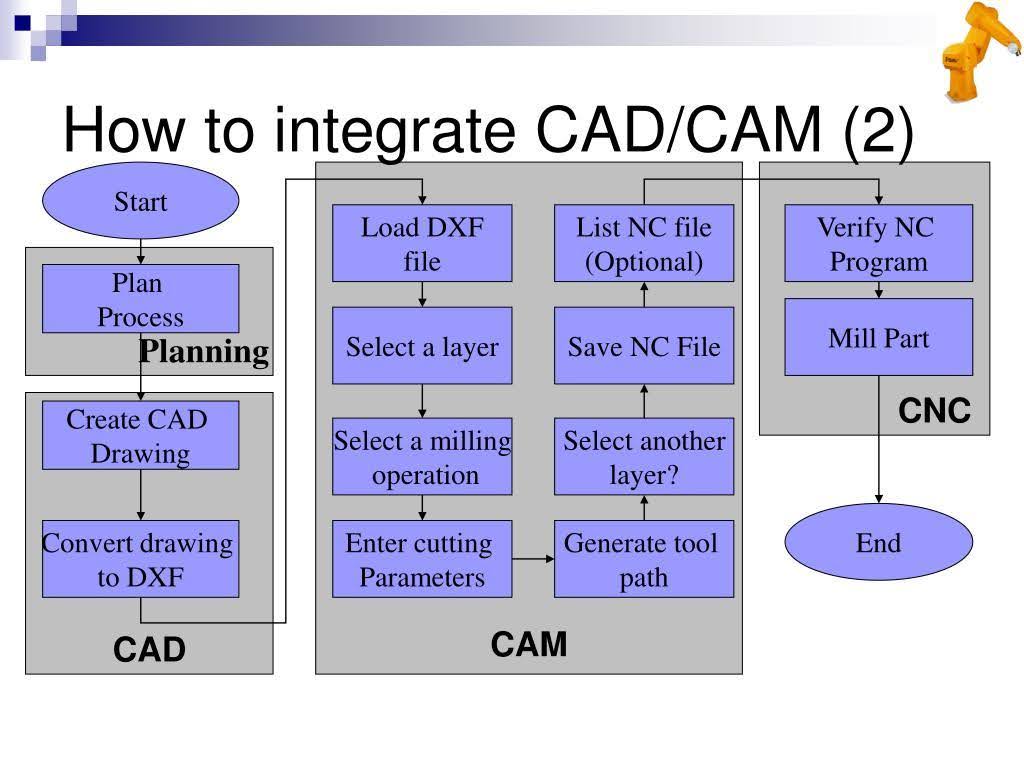
Tools: Software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Mastercam facilitate CAD/CAM integration.
CNC Machining
Mechanical engineers should know, how to conduct Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining processes for precision manufacturing.
-
Risk Assessment and Safety Engineering:
Mechanical engineers should know, how to identify and mitigate potential hazards in mechanical systems to ensure safety.
Failure Analysis
Investigating the causes of mechanical failures and developing strategies to prevent recurrence.
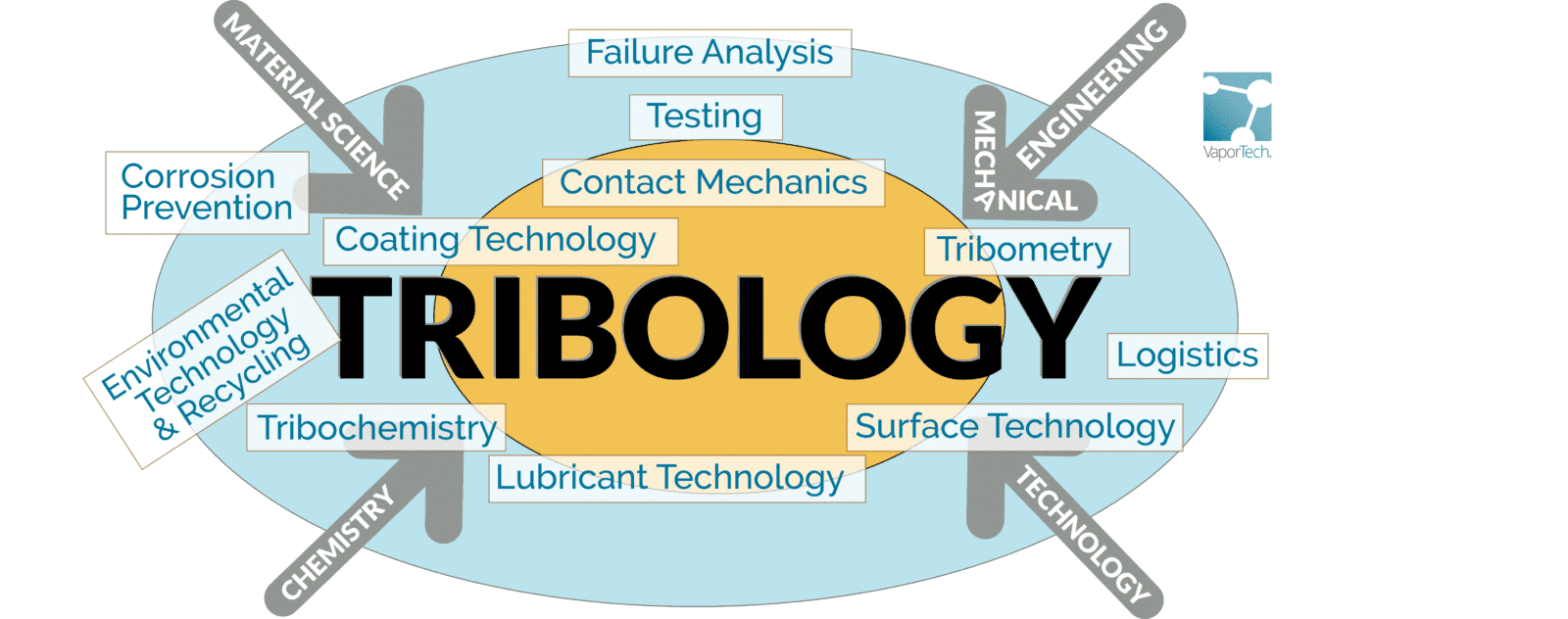
Tribology
Understanding friction, wear, and lubrication in mechanical systems to optimize performance and durability.
Composite Materials
Knowledge of designing and working with composite materials for lightweight and high-strength applications.
Data Analysis and Analytics
Mechanical engineer should know, use of data analysis tools for performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and decision-making.
Professional Certifications
Obtaining relevant certifications in areas such as project management, CAD software, or specialized engineering fields.
Soft Skills
Developing soft skills such as teamwork, leadership, and adaptability for effective collaboration in diverse work environments.
-
Supply Chain Management:
Understanding the logistics and supply chain aspects related to manufacturing and production.
Simulation and Modeling: Using simulation software for predicting and optimizing the behavior of mechanical systems.
Quality Control
Implementing quality control measures to ensure products meet specified standards.
Mathematics and Numerical Methods
Strong mathematical skills and the ability to use numerical methods for analysis and problem-solving.
Human Factors Engineering
Considering human factors in the design of products and systems to enhance usability and safety.
International Standards
Familiarity with relevant industry standards and regulations applicable to specific projects.
Entrepreneurial Skills
For those interested in starting their ventures, knowledge of business and entrepreneurship can be valuable.
“Join Ken Institute for comprehensive Mechanical Engineering courses led by expert faculty, ensuring your readiness to tackle workplace fire emergencies effectively.”
The knowledge of these additional areas provides a snapshot of the depth and application of each area for mechanical engineers. Depending on your interests and career goals, you may choose to specialize in one or more of these areas within mechanical engineering.
Continuous learning, hands-on experience, and staying updated on industry advancements are essential for a successful and fulfilling career in this dynamic field.
To gain the advanced acumen and skills needed to make your career stand out, join online courses in Mechanical Engineering. Take advantage of the expert faculty’s vast research experience and the flexibility of 100% online learning. Join Ken Institute and unlock a world of online courses in Mechanical Engineering, Occupational Health and Safety, Fire Safety, and Environment and Sustainability. Propel your career to new heights.
Schedule a call with one of our admissions outreach advisors today at +917569034271
Get in touch with us at: info@keninstitute.com
Visit our website: www.keneducation.in
Let’s connect on Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, and Instagram.


