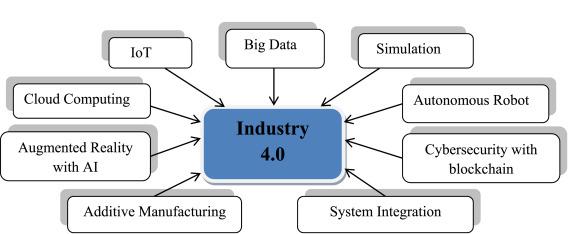
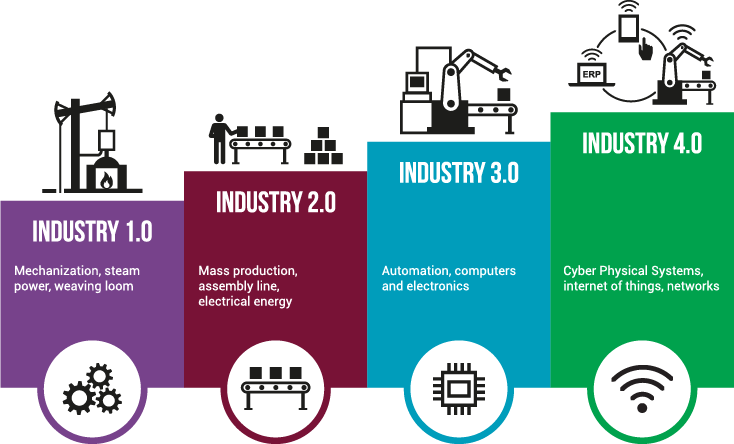
Industry 4.0, often referred to as the fourth industrial revolution, is characterized by the integration of digital technologies, data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) into various aspects of manufacturing and industry. “The impact of Industry 4.0” on mechanical engineering is significant in transforming traditional manufacturing processes and systems.
Key aspects of “impact of Industry 4.0” on Mechanical Engineering
-
Smart Manufacturing and Connectivity:
Mechanical engineering is at the forefront of designing and implementing smart manufacturing systems, which often involve the integration of sensors, actuators, and communication technologies into machinery.
Industry 4.0 introduces the concept of smart manufacturing, where machines, systems, and processes are interconnected and can communicate with each other. This connectivity allows for real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes.
In the context of mechanical engineering, smart manufacturing involves the integration of machinery, processes, and systems through the Internet of Things (IoT) and other connectivity solutions.
Mechanical engineers are tasked with designing and implementing communication protocols that allow machines to share data in real-time. This connectivity enables improved monitoring, control, and coordination of manufacturing processes.
-
IoT and Sensors:
The integration of sensors in mechanical systems enables the collection of real-time data on equipment performance, environmental conditions, and product quality.
Mechanical engineers play a crucial role in designing and incorporating these sensors into machines and processes. They need to have a deep understanding of sensor technologies and data analytics to optimize performance.
IoT devices and sensors are integral to Industry 4.0. Mechanical engineers work on incorporating these devices into machines and systems to collect data on various parameters such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and more.
The impact of Industry 4.0 is the real-time data that is invaluable for predictive maintenance, as mechanical engineers can anticipate when a machine is likely to fail and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime.
-
Data Analytics and Big Data:
Industry 4.0 generates vast amounts of data through sensors and connected devices. Mechanical engineers need to harness this data for predictive maintenance, process optimization, and product quality improvement.
Knowledge of data analytics tools and techniques becomes essential for mechanical engineers to extract meaningful insights from the data generated by smart manufacturing systems.
The data generated by sensors and other connected devices form the basis of data analytics in Industry 4.0. Mechanical engineers need to have expertise in tools and techniques for processing and analyzing large datasets.
By leveraging data analytics, mechanical engineers can optimize manufacturing processes, improve energy efficiency, and enhance overall system performance.
-
Digital Twins:
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical systems, allowing engineers to simulate and analyze performance before, during, and after the manufacturing process.
Mechanical engineers use digital twins to model and simulate the behavior of mechanical components and systems, facilitating design improvements and optimization.
-
Automation and Robotics:
This is a very important impact of Industry 4.0 which helps in emphasizing the use of automation and robotics for increased efficiency and productivity.
Mechanical engineers are involved in the design, programming, and maintenance of robotic systems used in manufacturing. This includes collaborative robots (cobots) that can work alongside human operators.

-
Digital Twins and Simulation:
Digital twins involve creating virtual replicas of physical systems. Mechanical engineers use digital twins to simulate the behavior of machines and components under different conditions.
This simulation allows for predictive analysis, design optimization, and testing without physical prototypes, saving time and resources in the product development lifecycle.
-
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing):
Additive manufacturing technologies have gained prominence in Industry 4.0. Mechanical engineers are involved in the design and optimization of components for 3D printing.
The flexibility of additive manufacturing allows for rapid prototyping, customization, and the creation of complex geometries that may be challenging with traditional manufacturing methods.
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, revolutionizes traditional manufacturing methods. Mechanical engineers play a crucial role in designing components suitable for 3D printing.

They need to consider material properties, structural integrity, and the unique capabilities of additive manufacturing to create innovative and optimized designs.
-
Cybersecurity in Manufacturing:
With increased connectivity, the importance of cybersecurity in manufacturing becomes paramount due to the Impact of Industry 4.0. Mechanical engineers need to consider cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of smart manufacturing systems.
As manufacturing systems become more connected, the risk of cybersecurity threats increases. Mechanical engineers need to be aware of cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of manufacturing processes.
This includes implementing secure communication protocols, access controls, and regularly updating and patching software to guard against potential cyber attacks
-
Human-Machine Interaction:
Industry 4.0 impacts how humans interact with machines. Mechanical engineers play a role in designing user interfaces, ergonomic considerations, and collaborative work.
In smart manufacturing environments, human-machine interaction becomes critical. Mechanical engineers are involved in designing interfaces that facilitate seamless interaction between humans and machines.
This includes considering ergonomics, user-friendly interfaces, and ensuring that human operators can effectively collaborate with automated systems.
Summary
The impact of Industry 4.0 on mechanical engineering is substantial, requiring professionals in the field to adapt to new technologies, acquire additional skills in data analytics and cybersecurity, and actively contribute to the development and implementation of smart manufacturing solutions.
The evolving landscape of Industry 4.0 requires mechanical engineers to be interdisciplinary in their approach, combining traditional mechanical engineering knowledge with expertise in electronics, software, data analytics, and cybersecurity. Adaptability and a willingness to embrace new technologies are key for professionals in the field to thrive in this era of advanced manufacturing.
“Join Ken Institute for comprehensive Mechanical Engineering Courses led by expert faculty, ensuring your readiness to tackle workplace fire emergencies effectively.”
We are here to expand your perception around Mechanical Engineering, Environment, and Sustainability & the health and safety topic.
join us at info@keninstitute.com
visit our website at www.keneducation.in
call at +917569034271


